Everything the beginner needs to know about ETH staking
Since the 1500s, banks dominated the monetary economy by becoming a centralized system of trust. When people wanted to conduct transactions, they would fall back on banks to act as the source-of-truth ledger.
The genius of cryptocurrencies, however, enables users to bypass the middlemen and send money to one another through a distributed ledger, maintained by a network of autonomous computers. This has resulted in a decentralized system of trust that operates independently of any one institution.
Staking is fundamental to forging new blocks in networks that use Proof-of-Stake for validating transactions.
Validating transactions: Crypto vs Fiat
The main selling point of cryptocurrencies is that they allow you to send money peer-to-peer, without the involvement of third parties. This is different from government-issued currencies like USD and Euros, for which we rely on trusted third-party entities like governments and banks to regulate their value and flow in the economy.
![[object Object]](https:////images.ctfassets.net/nccdc912q1to/5Q9avwPJiEk1UEWSHGGxH2/0d529aa0be302489c19c540208e27992/Validate_transaciton.png)
Strong advocates of cryptocurrencies are passionate about crypto facilitating the independence of money transfer. This is because no third party can intervene in where or who you send your funds to.
When Person A sends money to Person B, we need to ensure the following:
Authenticity: The right sender is transferring the money
No double spending: The money is not fake
Because this required trusted third-parties in the past, we developed big institutions like banks, Western Union, and PayPal to ensure that our money transfers are valid.
But with blockchains, consensus mechanisms autonomously do the work that banks do in payments.
Consensus Mechanisms & Proof of Stake
While there are multiple consensus mechanisms existing today, the most popular ones are Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and Proof-of-Work (PoW). These are different mechanisms that validator nodes use to determine if a transaction is valid. If the network determines that the transaction is valid, its block will be forged on the blockchain forever.
Further Reading: Centralized VS Decentralized Ledgers Trusting blockchain VS Centralized authorities
You might have heard that Ethereum is moving to the PoS mechanism. This is because PoS uses far less energy, which makes it a better scaling solution for the Ethereum network.
As the Ethereum network migrates to the PoS mechanism, users who hold ETH have the ability to stake their ETH.
How Proof-of-Stake works
PoS requires holders to stake their token in exchange for the opportunity to validate transactions for the blockchain. This requires them to lock their funds away in the network's staking contract so that those tokens can be used as collateral for giving the node an opportunity to become a validator of the next block.
How PoS validation works (using Ethereum as an example)
The PoS algorithm selects a node to be the validator from a selection of validators who have staked their ETH. The chances of a validator getting selected to validate the next block depends on:
Staking age: How long the ETH has been staked for
Randomization: Random selection of a node
Node's wealth: Amount of ETH staked
Generally, the higher the amount you stake, the more likely your node will get chosen for validating a transaction. In order to ensure that the mechanism does not unfairly always prize nodes that have more ETH, the 2 other factors above are considered for choosing the successful validating node.
When a node gets chosen to forge the next block, it will check if the transaction in the block is valid and add them to a shard block. Once the shards are validated, the block is added to the blockchain. As a reward, the node receives the transaction fees that are associated with the transactions in the block.
What if the transaction is fraudulent?
The forger node will lose a part of its stake and its right to participate as a forger in the future. Since validators are chosen based on the amount that they stake in the network, the cost of losing their staked funds is much higher than the cost of running the node. This puts in a solid incentive system for validators to operate as good actors in the system.
Further Reading: Proof of Stake
Should you stake ETH?
For beginners, staking ETH is a suitable gateway to DeFi. At the same time, this is your opportunity to contribute to the Ethereum network. There were more than 500,000 Ethereum addresses that were active on the blockchain in January 2022. Most people who hold ETH let it lie around without doing anything with it. Staking is one way to earn passively through your ETH.
Here are 3 reasons some ETH holders stake their ETH:
Support Operations
![[object Object]](https:////images.ctfassets.net/nccdc912q1to/3zVXQVaEBBbyo2mPf5PJTS/fea0f8478ae96443c16f7949c81ccc66/eth-1.png)
Source: Ethereum Foundation
Being a validator gives you the opportunity to contribute to the operation of the Ethereum blockchain. Many ETH stakers are avid supporters of the Ethereum network. Ethereum was built on the ethos of digital freedom and built a digital economy that is open to everyone. Validators are proud to participate in maintaining the security of the network. You can also be a part of that by staking your ETH.
Earn Rewards
![[object Object]](https:////images.ctfassets.net/nccdc912q1to/6XAfbASkFXjaA0ZV35S3iY/ddb8eb17b72b1332741b15fef6be770d/ETH-token.png)
Source: Etheruem Foundation
Staking Ethereum is a form of passive earning for investors who are already holding Ethereum. On the date of this writing, investors can make 4.26% annualized returns on their ETH by staking through the ETH staking pool, Lido via Omni. Stakers are rewarded in ETH every few days, which is particularly attractive for holders who believe in the Ethereum network and believe that its value will increase over time.
Enter DeFi
![[object Object]](https:////images.ctfassets.net/nccdc912q1to/3fjA4smtbwRoeUjSMQqHd6/ba2627da7c1504bb951c5e49f5fb7119/what.is.ethereum.1.jpg)
Source: Ethereum Foundation
As a beginner, staking ETH is an easy first-step to DeFi because staking ETH (particularly, liquid staking ETH) gives you the opportunity to interact with decentralized protocols. They also provide you with liquid ETH (e.g. stETH), which you can use in DeFi protocols to create more yield.
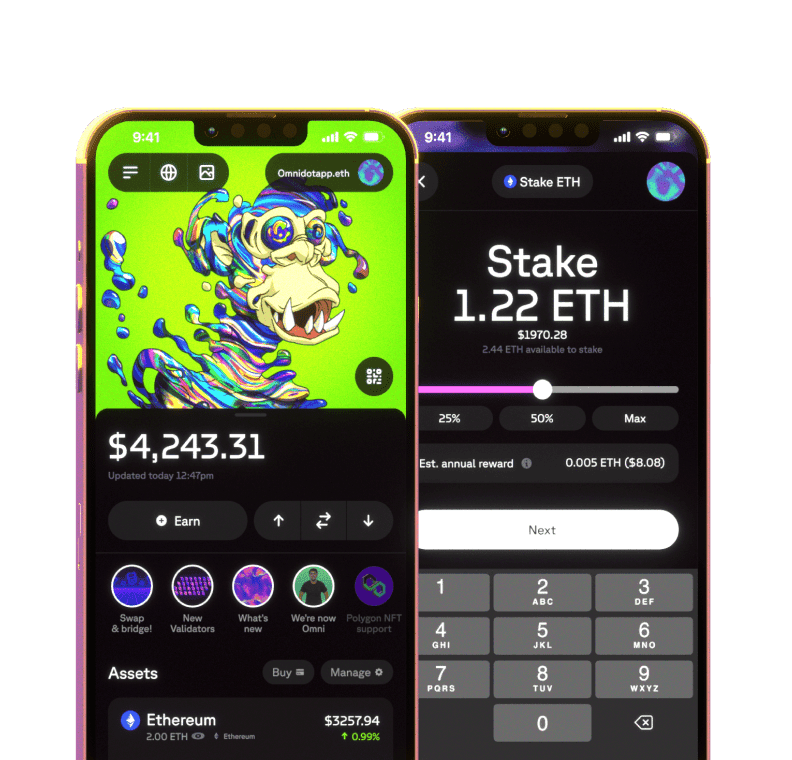
Staking your ETH is very simple if you use the right tools!
How to stake ETH
The easiest way to stake Ethereum in Web 3 is through the Omni app. After you pull your funds into your Omni wallet, you can stake your ETH with just 3 taps!
![[object Object]](https:////images.ctfassets.net/nccdc912q1to/7mVr2gny5lVtYDb1oFPdgT/d083e886f29e541ead51604bf93d4b67/stake-eth--1-.png)
Omni uses Lido to allow users to:
Stake any amount of ETH
Get stETH in exchange for their staked ETH, which means that their ETH will not be locked as stETH is pegged 1:1 to ETH
![[object Object]](https:////images.ctfassets.net/nccdc912q1to/2mJ6VeHlXxtG5znNXbu0Zn/d7befbfd4995a4a181501f4765e7c78d/Liquid-Stake-ETH_steakwallet-1.png)
Onboard to the Ethereum ecosystem
ETH staking beginners are looking for ways to earn more with their ETH. The Steakwallet Explore Screen showcases the best dApps in the Ethereum ecosystem that will allow them to just do that. Whether you choose play-to-earn games to earn extra returns or farm additional yield through AMMs, the explore screen gives you the hottest projects to maximize rewards and fun!
![[object Object]](https:////images.ctfassets.net/nccdc912q1to/6MKNsFMgV5Ppsj0PK44O0U/a330e034cdf6a7b3f108392b0d45e9cb/explore-screen-4.png)
Get a taste of the hottest findings of Steakwallet's Explore screen:
FAQ
Should I stake ETH before or after the merge?
If you are staking 32ETH as a validator, then your ETH will be locked for an unknown period of time, even after the merge. Although Ethereum plans to enable unstaking in the future, the developers have not specified when that option will be available. If you are staking through a staking pool, staking before or after the merge does not matter as much. However, here are 2 points for you to consider:
As the number of ETH stakers increase, the rewards rate decreases. With the merge, Ethereum expects the number of validators in the network to increase notably. This means that you should expect to earn lower rewards as time progresses.
Some ETH holders prefer waiting till after the merge to stake their ETH to ensure that the new PoS system is secure and functional.

 Susma -
Susma -